A warning from provincial officials as temperatures continue to climb across the region.
A notice from the Ministry of Health is urging residents to take precautions to prevent tick bites and reduce the risk of Lyme disease and other tick-borne illnesses when enjoying the outdoors.
Lyme disease is an infection that comes from being bitten by an infected blacklegged tick, also known as a deer tick. Symptoms include fever, headache, muscle and joint pain, fatigue, and an expanding circular rash that looks like a bulls-eye.
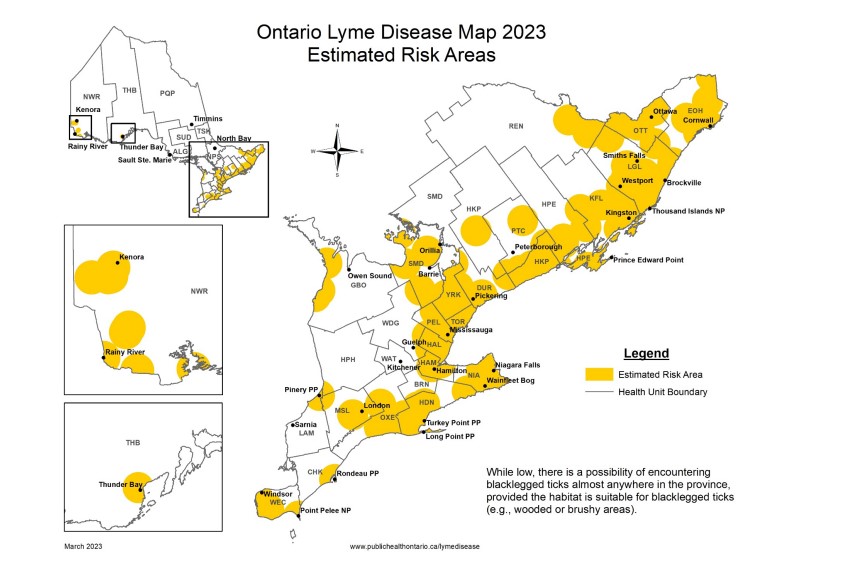
Rondeau Provincial Park and Point Pelee National Park have been listed as areas of risk for Lyme Disease.
Ticks commonly live in wooded areas, tall grasses, and bushes and can be found almost anywhere in Ontario, including city gardens and parks.
If bitten by an identified blacklegged tick from this high-risk area, and it has been attached and feeding for more than 24 hours, it is recommended that you consult a health care provider.
Protect yourself against tick bites. Besides routine tick checks after outdoor activities, you can protect yourself against tick bites by:
- Covering up with long, light coloured tops and pants as well as closed-toe shoes
- Use insect repellent with DEET or icaridin
- Stick to marked trails and avoid densely wooded areas or areas with high grassEarly symptoms of Lyme disease appear 3 to 30 days after a bite by an infected blacklegged tick. Most people experience flu-like symptoms, including:
- A rash at the site of the tick bite (sometimes shaped like a bullseye)
- Fever
- Chills
- Headache
- Muscle and joint pain
- Swollen lymph nodes
If Lyme disease is not treated, additional symptoms can appear months or even years later. These include:
- Additional skin rashes
- Severe headaches
- Facial paralysis
- Heart palpitations or irregular heartbeat
- Dizziness or shortness of breath
- Confusion, memory loss and inflammation of the brain or spinal cord
- Shooting pains, numbness or tingling in hands and feet
- Arthritis and severe joint pain and swelling




